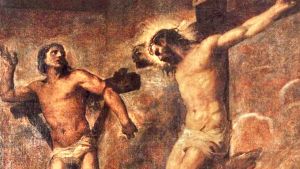don Giuseppe Nespeca
Giuseppe Nespeca è architetto e sacerdote. Cultore della Sacra scrittura è autore della raccolta "Due Fuochi due Vie - Religione e Fede, Vangeli e Tao"; coautore del libro "Dialogo e Solstizio".
Second Sunday of Advent (year A) [7 December 2025]
May God bless us and may the Virgin protect us! From this Sunday onwards, in addition to the summary of the most important elements of each reading, I will add a brief commentary on the Gospel by a Father of the Church.
*First Reading from the Book of the Prophet Isaiah (11:1-10)
Isaiah speaks of the root of Jesse and refers to the descendants of King David. Jesse had eight sons, but God chose Samuel not to choose the strongest or the eldest, but the youngest: David, the shepherd, who became the greatest king of Israel. From that moment on, Jesse became the progenitor of a dynasty often represented as a tree destined for a great future, which would never die. The prophet Nathan promised David that his descendants would reign forever and bring unity and peace to the people. But in history, the kings of his lineage did not fully keep these promises. However, it is precisely from disappointments that a stronger hope arises: if God has promised, then it will come to pass. How did the idea of the Messiah come about? The term 'messiah' (in Hebrew mashiach = 'anointed') originally referred to any king, because he was 'anointed' with oil on the day of his coronation. Over time, however, the word 'messiah' took on the meaning of 'ideal king', the one who brings justice, peace and happiness. When Isaiah says, 'A shoot will come up from the stump of Jesse', it means that even if David's dynasty seems like a dead tree, God can bring forth a new shoot, an ideal king: the Messiah, who will be guided by the Spirit of the Lord. The seven gifts of the Spirit, symbols of fullness, will rest upon him: wisdom, understanding, counsel, fortitude, knowledge, and the fear of the Lord, which is not fear but trust and respect as a son. The Messiah will rule as God wills: with justice and faithfulness, and his task will be to wage war on injustice: He will judge the poor with justice... not according to appearances... he will put an end to wickedness with the breath of his lips. 'The wicked' does not refer to a person, but to wickedness itself, like saying 'waging war on war'. Isaiah describes a world where the wolf lives with the lamb, the child plays without fear, there is no more violence or conflict. It is not a return to paradise on earth, but the final fulfilment of God's plan, when the knowledge of the Lord will fill the earth. The root of Jesse will be a sign for all peoples, and the Messiah concerns not only Israel but all nations. Jesus himself will take up this idea: "When I am lifted up from the earth, I will draw all people to myself" (Jn 12:32). Isaiah preaches in the eighth century BC, at a time of political pressure and threats from neighbouring empires. The tree of David seems to be dead, but Isaiah urges us not to lose hope. The "animal fable" uses symbols to speak of human beings, as La Fontaine would do many centuries later, and constitutes a promise of peace, brotherhood and universal reconciliation. Martin Luther King, in his "I have a dream" speech, drew direct inspiration from these images used by Isaiah (cf. 11:2): a world where justice and brotherhood overcome violence.
The central theme can be summed up in one sentence: From the seemingly dead trunk of David's dynasty, God is so faithful that, when all seems lost, he revives his promise from a fragment, from a stump: hope is born precisely where man can no longer see anything. God will raise up a Messiah guided by the Spirit, who will fight injustice and bring universal peace to all peoples. God is faithful, and even from a dead trunk he can bring forth new life. It is messianic peace, the final reconciliation of creation. There are times when we too feel like a cut tree: failures, disappointments, repeated sins, broken relationships, projects that do not come to fruition, communities that seem to be losing strength. Isaiah announces: God is not finished with you either, and even where you see no future, He sees a sprout. Continue to hope, because God sees sprouts where we see only dry wood.
*Responsorial Psalm (71/72, 1-2, 7-8, 12-13, 17)
Psalm 71/72 is a prayer that arose after the Babylonian exile, at a time when there was no longer a king in Israel. This means that the psalm no longer speaks of an earthly ruler, but of the king promised by God: the Messiah. Since it is God who promises him, his fulfilment is certain. The entire Bible is permeated with an indestructible hope: history has meaning and direction, and God has a plan of happiness for humanity. This plan takes on different names (the Day of the Lord, the Kingdom of Heaven, the benevolent plan), but it is always the same: like a lover who repeats words of love, God tirelessly proposes his plan of salvation.
This plan is announced from the beginning, in the vocation of Abraham (Gen 12:3): 'All the families of the earth shall be blessed in you'. The revelation is therefore universal from the outset. Israel is chosen not to manage a privilege, but to be a service and a sign for all peoples. The psalm takes up this promise: in the Messiah, all nations will be blessed and will call him blessed. It also takes up the other promise made to Abraham (Gen 15:18), namely the gift of the land "from the river of Egypt to the great river". Echoing this, the psalm says: "He shall rule from sea to sea and from the River to the ends of the earth." The book of Sirach (Sir 44:21) confirms this reading, linking together universal blessing, multiplication of descendants and extended inheritance. Although today the idea of a universal ruler may seem far removed from democratic sensibilities, and indeed there is fear of the imposition of a hidden world authority that would dominate the whole of humanity, the Bible reminds us that every ruler is only an instrument in the hands of God, and what matters is the people, considering the whole of humanity as one vast people, and the psalm announces a pacified humanity: In those days, justice will flourish, great peace until the end of time, poverty and oppression defeated. The dream of justice and peace runs through the entire Scripture: Jerusalem means 'city of peace'; Deuteronomy 15 states that there will be no more poor people. The psalm fits into this line: the Messiah will help the poor who cry out, the weak without help, the miserable who have no defence. The prayer of the psalm does not serve to remind God of his promises, because God does not forget. Instead, it serves to help man learn to look at the world through God's eyes, remember his plan and find the strength to work towards its realisation. Justice, peace and the liberation of the poor will not come about magically: God invites believers to cooperate, allowing themselves to be guided by the Holy Spirit with light, strength and grace.
Important points to remember: +Psalm 72 is messianic: written when there were no more kings, it announces the Messiah promised by God.+History has meaning: God has a plan of happiness for all humanity.+The promises to Abraham are the foundation: universal blessing and inheritance without borders.+The Messiah will be God's instrument, serving the people and not power.+The world to come will be marked by justice, peace and an end to poverty. +Prayer is not meant to convince God, but to educate us: it opens our eyes to God's plan. Peace and justice will also come through human commitment guided by the Spirit.
Second Reading from the Letter of Saint Paul to the Romans (15:4-9)
Saint Paul writes to the Romans: 'Everything that was written before us was written for our instruction... so that we may keep hope alive'. This sentence is the key to reading the entire Bible: Scripture exists to enlighten, liberate and give hope. If a text seems obscure or difficult, it simply means that we have not yet fully understood it: the Good News is always present and we must dig to find it, as if it were a hidden treasure. Scripture nourishes hope because it proclaims on every page a single plan of God: that "merciful design" which is the great love story of God with humanity. The entire Bible, from the Old to the New Testament, has only one subject: the plan of salvation and communion that God wants to realise in the Messiah. Paul then moves on to a concrete theme: the Christians in Rome were divided. There were two groups: Christians who came from Judaism and were still attached to Jewish religious and dietary practices, and Christians who came from paganism and considered such observances outdated. This diversity gave rise to discord, mutual judgement and suspicion. Liturgical and cultural differences became real conflicts. This situation is very similar to the tensions that exist even today in the Church between different sensibilities. Paul does not propose dividing the community into two separate groups. Instead, he proposes the path of cohabitation, the building of peace, patience and mutual tolerance, inviting everyone to seek what promotes peace and what builds up the community. Let each one seek the good of the other, and may 'the God of perseverance and consolation' grant you to live in harmony according to Christ. The fundamental principle is: 'Welcome one another as Christ has welcomed you'. Paul recalls that Christ took upon himself the mission of the Servant of God announced by Isaiah: chosen and elected by God, formed every morning by the Word, giver of his own life, bringer of salvation to all nations. Christ, by dying and rising again, united the Jews, saved in continuity with their Covenant, and the pagans, saved by God's gratuitous mercy. For this reason, no one can claim superiority; rather, everything is grace, everything is a gift from Christ, and true worship is this: to overcome the past, to recognise the gift received, to welcome one another without distinction, to sing together of God's faithfulness and mercy.
Important elements to remember: +Scripture exists to give hope. Every page of the Bible is Good News. If we do not find liberation, we have not yet understood the text. + The Bible proclaims a single plan. God's "providential plan" is to bring humanity to communion and salvation through the Messiah. +Paul corrects a divided community: In Rome, there were tensions between Christians of Jewish and pagan origin. Practical and cultural differences created judgements and conflicts. The Christian solution is not to separate. Paul proposes cohabitation, patience, and mutual edification. The community is a 'building' that must be constructed with peace and tolerance. +The model is Christ the Servant who united everyone: Jews and pagans. No one can boast: everything is grace. +The watchword: welcome: Welcome one another as Christ has welcomed you. The Church is alive when it overcomes divisions and lives mercy.
*From the Gospel according to Matthew (3:1-12)
When John the Baptist begins his preaching, Judea has been under Roman rule for 90 years, Herod is in power but deeply hated; religious currents are divided and confused; there are collaborators, resisters, false prophets, messianic agitators. The people are tired and disoriented, and it is in this climate that the preaching of John, who lives in the desert of Judea (between Jerusalem and the Jordan), begins. Matthew insists on the spiritual meaning of the desert: he recalls the Exodus, the Covenant, purification, the loving relationship between God and Israel (Hosea) and sees the desert as the place of return to truth and decision. In John, everything recalls the great prophets: he wears camel's hair, eats locusts and honey, and lives an ascetic lifestyle. Many consider him the possible return of Elijah, awaited to prepare for the coming of God (Malachi 3:23). His preaching has a double prophetic tone: sweet and comforting for the humble; harsh and provocative for the proud. The expression "brood of vipers" is not a personal insult, but a way of saying, "you are following the logic of the tempting serpent," and is therefore an invitation to change one's attitude. John invites everyone to make a righteous discernment in their lives: what is healthy remains, what is corrupt is eliminated. And to be incisive, he uses strong images: fire burning straw (a reference to the prophet Malachi), a sieve separating wheat from chaff, a threshing floor where the choice is made - and this is the meaning: everything in us that is death will be purified; everything that is authentic will be saved and preserved. It is a liberating judgement, not a destructive one. John announces Jesus: 'I baptise you with water, but the one who comes after me... will baptise you with the Holy Spirit and fire'. Only God can give the Spirit, and so John implicitly affirms the divinity of Jesus. The images used: 'Stronger than me' is a typical attribute of God. "I am not worthy to carry his sandals or untie his sandals": with this he recognises Jesus' divine dignity. Although he is a teacher followed by disciples, John puts himself in the second row; he recognises Jesus' superiority and paves the way for the Messiah. His greatness consists precisely in making room. Matthew shows him as a "voice in the desert" with reference to Isaiah 40:3, also linked to Elijah (2 Kings 1:8; Malachi 3:23), in the line of prophets to introduce Jesus as God present and judge. Chapters 3-4 of Matthew are a hinge: here begins the preaching of the Kingdom.
Important elements to remember: +John appears in a context of oppression and moral confusion: his word brings light and discernment. +The desert is a place of new covenant, truth and conversion. +John presents himself with prophetic signs (clothing, food, style) reminiscent of Elijah. +His preaching is twofold: consolation for the little ones, provocation for those who are sure of themselves. +Judgement is internal, not against categories of people: it purifies the evil in each person. Fire does not destroy man, but what is dead in him: it is a fire of love and truth. +Jesus accomplishes purification by baptising in the Holy Spirit, something that only God can do, and John recognises the divinity of Jesus with gestures of great humility. +The greatness of the Precursor lies in stepping aside to make room for the Messiah, and Matthew places him as a bridge between the Old and New Covenants, inaugurating the preaching of the Kingdom.
St John Chrysostom – Commentary on Matthew 3:1-12
'John appears in the desert not by chance, but to recall the ancient path of Israel.
Israel was educated in the desert, and now conversion begins again in the desert. His rough clothing and simple food show that he is free from all vanity, like Elijah. For this reason, the people, tired of the leaders of the time, flock to him: they see in John a truthful man who does not seek glory but leads to the truth." Chrysostom then explains the prophetic and moral content of John's preaching: By calling them a 'brood of vipers', he is not insulting them, but shaking them up so that they realise the poison that corrupts them. He does not attack people, but the evil that possesses them.
The judgement he announces is not against men, but against their evil deeds: fire burns guilt, not human nature." And regarding the announcement of the Messiah: "By saying, 'One more powerful than I is coming after me,' John does not compare himself to another man, but to God. For only God is said to be the Strong One. And when he adds, 'He will baptise you with the Holy Spirit', he openly confesses that the One who is coming has divine power. For this reason, he declares that he is not even worthy to untie his sandals: not because he despises himself, but because he recognises the greatness of Christ." Finally, Chrysostom interprets the mission of the Precursor:
"His greatness consists in diminishing so that Christ may grow. He is the voice that prepares the Word; he is the bridge that connects the Old Covenant to the New. He shows that all that the prophets awaited is now fulfilled: the King is near, and the Kingdom begins."
+Giovanni D'Ercole
OBSESSION AND COMPULSION - (by Francesco Giovannozzi, psychologist and psychotherapist)
Obsession and Compulsion
A gentleman confides in me that for some time now he has felt the need to check whether he has locked the front door of his house. A lady, on the other hand, needs to be sure that she has turned off the gas in the kitchen.
After checking, both the gas and the front door were fine and in order.
Another middle-aged man feels the need to see if his car is okay, then he has to go and check it, walk around it, touch it in different places, and only after completing these behavioural sequences can he return home peacefully. Sometimes he feels the need to do this several times a day.
In the Treccani dictionary, the term 'obsession' is defined as: 'a mental representation that the will cannot eliminate, accompanied by anxiety'.
The term 'compulsion' is defined as: 'compulsion, being driven by necessity to do something'.
Many people have thoughts that they have no interest in; these are often ideas that make no sense, but which require considerable mental effort.
Without wanting to, these ideas invade our minds and make our brains 'rack' as if they were fundamental issues.
These may be thoughts or images that cause concern, and are usually followed by compulsions that the person must perform to calm their anxiety.
Between the 'fixed' idea and the need to perform some act or gesture to ensure that nothing bad happens, doubt often arises, undermining our most certain convictions.
This leads to increasing indecision, which limits our freedom of action: even simple choices take a long time to make.
Sometimes it leads us to be unable to make a decision. The doubt may concern a thought, a memory, an action, etc., and may spill over from one content to another.
A person with these problems, when leaving the house, sometimes feels compelled to return to make sure they have not left the light on, and to be sure, they sometimes have to do this several times.
In literature, there are examples of people who, after sending a letter, felt the need to reopen it to check what they had written.
In psychological contexts such as this, we also talk about 'rumination', which is always associated with doubt.
In biology, it refers to the digestive process of certain animals, such as cattle. Food that has been swallowed is brought back into the mouth to be chewed again, more thoroughly, and then swallowed again to complete digestion.
In psychology, 'rumination' describes repetitive and persistent thinking focused on past events, as opposed to 'brooding', which is more concerned with future events.
Ceremonials are also described. In these, the individual must perform a sequence of acts such as washing their hands frequently or cleaning everyday objects many times.
This is where an aspect of the psychological picture described comes into play: 'rupophobia' and contamination. Rupophobia is a morbid fear of dirt and of being infected. It can affect any aspect of our lives: objects, people or public places. It is an aspect that can also harm intimacy.
The Covid period has increased the fear of contagion, but this was a real event. Many years ago, around 1986, there was the Chernobyl phenomenon, and there we really had to be careful about what we ate because food, especially vegetables, could have been contaminated.
Anyone who has these ideas may count the cars in the car park while walking, or touch lampposts, or try to avoid cracks in the pavement, etc.
In severe cases, these people may feel that they are harming someone, so these thoughts make them 'back away'. They need to give themselves a 'shake' to try to dispel these terrifying ideas.
People with these characteristics are generally strict, concerned with details, and meticulous about rules and formalities.
However, by focusing on details, they often overlook the essentials.
How many people in their work environment feel the need to line up their objects in excessive order?
Order and control are closely interlinked, because external order can be a way of achieving internal order, which can reduce stress.
However, we are talking about excessive order. A minimum of order is necessary to avoid confusion and to be able to find our things.
Stuttering is also a speech disorder linked to this psychological condition.
The person who stutters struggles at the beginning, with the first letter or syllable, and repeats it until the word is finished.
As we know, their speech is fluent when they are alone or when they recite or sing.
Otherwise, mortified by their defect, they will tend to isolate themselves and speak as little as possible. Or they will stubbornly insist on speaking with intense physical effort.
Stuttering 'is a conflict between the erotic urethral tendency to expel and the erotic-anal tendency to retain, shifted to the mouth' (Manual of Psychiatry, Arieti, vol. I, p. 353).
Dr Francesco Giovannozzi, Psychologist-Psychotherapist.
First Sunday of Advent (year A) [30 November 2025]
May God bless us and may the Virgin Mary protect us! Advent marks the beginning of a new liturgical year (Year A), accompanied by the evangelist Matthew, who invites us to become collaborators in the plan of salvation that God has ordained for the Church and the world. A small change: from now on, I will also offer a summary of the main elements of each text.
First Reading from the Book of the Prophet Isaiah (2:1-5)
We know that biblical authors love images! Here are two beautiful ones in Isaiah's preaching: first, that of a huge crowd on the move, then that of all the armies of the world deciding to turn their weapons into agricultural tools. Let us look at these images one after the other. The crowd on the move climbs a mountain: at the end of the journey is Jerusalem and the Temple. Isaiah, on the other hand, is already in Jerusalem and sees this crowd arriving, a veritable human tide. It is, of course, an image, an anticipation, probably inspired by the great pilgrimages of the Israelites to Jerusalem during the Feast of Tabernacles (Sukkot). On this occasion, for eight days, people live in huts, even in the city, remembering their stay in the desert during the Exodus. All the Jewish communities flock there, and Deuteronomy invites them to participate with joy, even with their children, servants, foreigners, orphans, and widows (Dt 16:14-15). The prophet Isaiah, observing this extraordinary annual gathering, foresaw a future one and, inspired by the Holy Spirit, announced that one day not only Israel but all nations would participate in this pilgrimage and the Temple would become the gathering place for all peoples, because the whole of humanity would know the love of God. The text intertwines Israel and the nations: "The mountain of the Lord's temple will be raised above the hills... and all nations will flock to it." This influx symbolises the entry of other nations into the Covenant. The law will come forth from Zion and the word of the Lord from Jerusalem: Israel is chosen by God, but it also has a responsibility to collaborate in the inclusion of the nations in the divine plan. Thus, the Covenant has a dual dimension: particular (Israel chosen) and universal (all nations). The entry of the nations into the Temple does not concern sacrifice, but listening to the Word of God and living according to His Law: "Come, let us go up to the mountain of the Lord ... that He may teach us His ways and we may walk in His paths." The second image shows the fruit of this obedience: the nations will live in peace, God will be judge and arbiter, and weapons will be transformed into tools of labour: They will forge their swords into ploughshares and their spears into pruning hooks. They will no longer raise the sword against a people. Finally, Isaiah invites Israel to walk in the light of the Lord, to fulfil its vocation and to lead everyone towards the Light: going up to the Temple means celebrating the Covenant, walking in the light means living according to the Law.
In summary, here are all the main elements of the text:
+Two symbolic images from Isaiah: the crowd on pilgrimage and the transformation of weapons into instruments of peace.
+Jerusalem and the Temple: destination of the pilgrimage, symbol of God's presence and centre of the Covenant.
+Feast of Tabernacles (Sukkot): historical reference to the annual pilgrimage of the Israelites.
+Universality of salvation: Israel, the chosen people, guides all nations, which will be included in the Covenant.
+Dimension of the Covenant: particular (Israel) and universal (all nations).
+Listening to the Word and living according to the Law: participation is not only ritual, but a concrete commitment to life.
+Peace and transformation of weapons: symbol of the realisation of God's plan of justice and harmony.
+Final invitation: Israel must walk in the light of the Lord and lead humanity to God.
+Prophecy as promise, not prediction: prophets speak of God's will, not of the future in a divinatory sense.
Responsorial Psalm (121/122, 1-9)
Here we have the best possible translation of the Hebrew word "Shalom": "Peace to those who love you! May peace reign within your walls, happiness in your palaces...". When you greet someone with this term, you wish them all this. Here this wish is addressed to Jerusalem: 'Pray for the peace of Jerusalem... For my brothers and my friends, I will say: Peace be upon you! For the house of the Lord our God, I will pray for your good'. The very name Jerusalem contains the word shalom; it is, should be, and will be the city of peace. However, this wish for peace and happiness is still far from being realised. The history of Jerusalem is turbulent: around 1000 BC, it was a small village called Jebus, inhabited by the Jebusites. David chose this place as the capital of his kingdom: initially, the capital was Hebron, and David was king only of the tribe of Judah; then, with the accession of the other tribes, Jebus was chosen, which became Jerusalem, 'the city of David'. Here David transferred the Ark of the Covenant and purchased Araunah's field for the Temple, following God's will. The definition of Jerusalem as a 'holy city' means that it belongs to God: it is the place where one must live according to God. With David and Solomon, the city reached its cultural and spiritual splendour and became the centre of religious life with the Temple, a destination for pilgrimages three times a year, particularly for the Feast of Tabernacles. The prophet Nathan reminds David that God is more interested in the people than in the Temple: "You want to build a house for God, but it is God who will build a house for you (descendants)". Thus God promises to preserve David's descendants forever, from whom the Messiah will come. In the end, it was Solomon who built the Temple, making Jerusalem the centre of worship. The city then underwent destruction and reconstruction: the conquest by Nebuchadnezzar in 587 BC, the Exile to Babylon, the return authorised by Cyrus in 538 BC and the reconstruction of Solomon's Temple. Even after the persecutions of Antiochus Epiphanes and the destruction of the Temple in 70 CE, Jerusalem remained the holy city, symbol of God's presence, and the hope of its full restoration remained alive. Believers, wherever they were, continued to turn to Jerusalem in their daily prayers, remembering God's faithfulness to the promises made to David. Psalm 121/122, a pilgrimage song, celebrated this centrality of Jerusalem, inviting the faithful to ascend to the house of the Lord and walk in God's light.
Summary of main points
+Shalom and Jerusalem: Shalom means peace and happiness; Jerusalem is the city of peace.
+History of the city: from Jebus to David's capital, transfer of the Ark, construction of the Temple.
+Holy city: belongs to God; living in Jerusalem means living according to God.
+Nathan and the descendants of David: God more interested in the people than in the Temple; promise of the Messiah.
+Pilgrimages and religious life: Jerusalem as a centre of worship with pilgrimages three times a year.
+Destruction and reconstruction: Nebuchadnezzar, Exile, Cyrus, persecutions by Antiochus, destruction of the Temple in 70 AD.
+Hope and faith: Jerusalem remains a symbol of God's faithfulness; the faithful pray facing towards it.
+Psalm 121/122: a song of pilgrimage, inviting us to ascend to the house of the Lord and walk in divine light.
Second Reading from the Letter of Saint Paul the Apostle to the Romans (13:11-14)
In this text, Saint Paul develops the classic contrast between 'light and darkness'. 'Our salvation is nearer now than when we first believed'. This sentence remains true! One of the articles of the Catholic faith is that history is not a continuous repetition, but on the contrary, God's plan advances inexorably. Every day we can say that God's providential plan is further ahead than yesterday: it is being fulfilled, it is progressing... slowly but surely. To forget to proclaim this is to forget an essential point of the Christian faith. Christians have no right to be sad, because every day 'salvation is nearer', as Paul says. This providential and merciful plan of God needs us: this is no time to sleep. Those who know God's plan cannot risk delaying it. As the Second Letter of Peter says: "The Lord is not slow in keeping his promise... but is patient with you, not wanting anyone to perish, but everyone to come to repentance" (2 Pet 3:9). Our inactivity, our "sleep" has consequences for the fulfilment of God's plan; leaving our abilities dormant means compromising it or at least delaying it. That is why sins of omission are serious. Paul says, 'The night is far gone, the day is at hand'; and elsewhere he speaks of a short time, using a nautical term: the ship has set sail and is approaching the port (1 Cor 7:26, 29). It may seem presumptuous to think that our conduct affects God's plan, but this is precisely the value and seriousness of our life. Paul reminds us: 'Let us behave honourably, as in the daytime, not in orgies and drunkenness, not in sexual immorality and debauchery, not in quarrelling and jealousy'. There are behaviours of light and darkness when the baptised person does not live according to the Gospel. Paul does not only tell us to choose the works of light, but to reject those of darkness, always fighting for the light. This means two things: every day we must choose the light, a real struggle, especially in the face of anthropological and social challenges, forgiveness, and the rejection of compromises and privileges (cf. Phil 2:12). Elsewhere, St Paul also speaks of the armour of righteousness, the breastplate of faith and love, and the helmet of the hope of salvation (cf. 2 Cor 6:7; 1 Thess 5:8). Here, the garment of light is Jesus Christ himself, whose light envelops us like a cloak. In baptism, immersion symbolises death to sin and being clothed in Christ (Gal 3:27). The Christian struggle is not ours alone, but it is Christ who fights in us and promises us that when we are persecuted, we must not prepare ourselves because it is he who speaks to us and gives us wisdom that no one can oppose.
Summary of the main points
+Salvation is ever closer: history is not a cycle, but a progression of God's plan.
+Believers cannot be passive: our inactivity delays the fulfilment of God's plan, and sins of omission are serious because we must carry out God's plan every day.
+There are activities of light and darkness: Christian and non-Christian behaviours that do not always coincide with faith or baptism.
+The Christian struggle is daily: choosing light, forgiveness, rejecting compromise and immorality.
+The image of the robe of light represents Jesus Christ who envelops us and guides our lives. Baptism symbolises being clothed in Christ and the beginning of the struggle of light.
+The Christian's strength is not only his own: Christ fights in us, guaranteeing wisdom and words against persecution.
From the Gospel according to Matthew (24:37-44)
One thing is certain: this text was not written to frighten us, but to enlighten us. Texts like this are called apocalyptic, which literally means 'lifting a corner of the veil': they reveal reality. And the reality, the only one that matters, is the coming of Christ. Notice the language: coming, advent, always referring to Jesus: Jesus spoke to his disciples about his coming, which will be like in the days of Noah. You also do not know the day when the Lord will come, because it will be at the hour when you do not expect it. The heart of the message is therefore the announcement that Jesus Christ will come. Curiously, Jesus speaks in the future tense: 'Your Lord will come'. It would be more logical to speak in the past tense because Jesus had already come... This shows us that the 'coming' is not the birth, but something that concerns the fulfilment of God's plan. Very often we are disturbed by images of judgement, such as the comparison with the flood: "Two men will be in the field, one will be taken away and the other left." This is not divine arbitrariness, but an invitation to trust: just as Noah was found righteous and saved, so everything that is righteous will be saved. Judgement distinguishes the good from the bad, the wheat from the chaff, and this takes place in the heart of each person. Jesus uses the title Son of Man to speak of himself, but not only of himself as an individual: he takes up the vision of the prophet Daniel, in which the 'Son of Man' also represents the people of the saints, a collective being. Thus, the coming of Christ concerns the whole of humanity. As St Paul says, Christ is the head and we are the members; St Augustine speaks of the total Christ: head in heaven, members on earth. When we say in prayer that we await the good that God promises us, that is, the coming of Jesus Christ, we are referring to the total Christ: the man Jesus has already come, but the total Christ is in continuous growth and fulfilment. St Paul and, more recently, Teilhard de Chardin emphasise that the whole of creation groans in expectation of the fulfilment of Christ, which is progressively completed in history and in each one of us. When Jesus invites us to watch, it is an invitation to safeguard God's great plan, dedicating our lives to advancing it. Finally, this discourse takes place shortly before the Passion: Jesus warns of the destruction of the Temple, the symbol of his presence and of the Covenant, but does not answer specific questions about the end of the world; instead, he invites vigilance, reassuring his disciples in the face of trials.
Summary of the main points
+Purpose of the text: not to frighten, but to enlighten; to reveal the reality of Christ's coming.
+Christ's coming: Jesus speaks in the future tense because the complete coming concerns Christ as a whole, not just the historical birth of Jesus.
+Judgement and justice: distinguishing good from evil takes place in the heart of each person; the righteous will be saved.
+Title Son of Man: refers not only to Jesus, but to the people of the saints, that is, saved humanity. Christ in his entirety: Christ as the head and believers as members; fulfilment is progressive throughout history.
+Watchfulness and vigilance: the disciples are called to guard God's plan and dedicate their lives to its fulfilment.
+Temple and passion: the discourse precedes the Passion, announces the destruction of the Temple and invites the disciples to trust despite the trials they will have to endure.
Solemnity of Christ the King of the Universe [23 November 2025]
May God bless us and may the Virgin protect us. We close the liturgical year C with grateful hearts as we prepare to resume our journey with Advent.
*First Reading from the Second Book of Samuel (5:1-3)
These are the first steps of the monarchy in Israel. It all begins in Hebron, an ancient city in the mountains of Judea, where the patriarchs of Israel rest: Abraham and Sarah, Isaac and Rebecca, Jacob and Leah, and even Joseph, whose bones were brought back from Egypt. It is a place steeped in memory and faith, and it is here that David becomes king of all the twelve tribes of Israel. After the death of Moses, around 1200 BC, the people of Israel settled in Palestine. The tribes lived independently, united only by the memory of their liberation from Egypt and their faith in their one God. In times of danger, God raised up temporary leaders, the Judges, who guided the people and often also acted as prophets. One of these was Samuel, a great man of God. Over time, however, the Israelites wanted to be 'like other peoples' and asked Samuel for a king. The prophet was troubled by this, because Israel was to recognise only God as King, but in the end, on God's command, he consecrated Saul, the first king of Israel. After a promising start, Saul fell into disobedience and madness, and God chose another man: David, the young shepherd from Bethlehem, on whom Samuel poured the oil of anointing. David did not immediately take power: he served Saul faithfully, became his musician and valiant warrior, loved by the people and bound by deep friendship to Jonathan, Saul's son. But the king's jealousy turned to hatred, and David was forced to flee, while always refusing to raise his hand against 'the Lord's anointed'. After Saul's death, Israel was divided: David reigned in Hebron over the tribe of Judah, while in the north, one of Saul's sons reigned for a short time. When the latter was killed, the northern tribes gathered at Hebron and recognised David as their king. On that day, the united kingdom of Israel was born: twelve tribes under one shepherd, chosen by God and recognised by his brothers. The anointing with sacred oil made David the 'Messiah', that is, the 'anointed one of the Lord'. He was to be a king after God's own heart, a shepherd who would lead his people towards unity and peace. But history showed how difficult it was to realise this ideal. Nevertheless, hope did not die: Israel always waited for the true Messiah, the descendant of David who would establish an eternal kingdom. And a thousand years later, Jesus Christ, called "Son of David," presented himself as the Good Shepherd, the one who offers his life for his flock. Every Sunday, in the Eucharist, he renews his covenant and tells us: "You are of my own blood."
*Responsorial Psalm (121/122:1-2, 3-4, 5-6a, 7a)
"What joy when they said to me, 'We will go to the house of the Lord'." A pilgrim recounts his emotion: after a long journey, his feet finally stop at the gates of Jerusalem. We are in the time of the return from Babylonian exile: the city has been rebuilt, the Temple restored (around 515 BC), and the people find in the house of the Lord the living sign of the Covenant. Before the resurrected city, the pilgrim exclaims: Jerusalem, here you are within your walls, a compact city, where everything together forms one body! Jerusalem is not only a geographical location: it is the heart of God's people, a symbol of unity and communion. Every stone, every wall reminds us that Israel is a people gathered together by a single promise and a common destiny. God himself wanted Israel to make an annual pilgrimage to Jerusalem, so that the common journey and shared effort would keep the bond of the Covenant alive. This is why the Psalm proclaims: "There the tribes go up, the tribes of the Lord... to praise the name of the Lord." The verb "to go up" indicates both the elevated position of the city and the spiritual ascent of the people towards their liberating God, the same God who brought them up, that is, out of Egypt. The phrase 'the tribes of the Lord' recalls the mutual belonging of the Covenant: 'You shall be my people, and I will be your God.' The pilgrimage, made on foot, amid fatigue, thirst and songs, is a journey of faith and fraternity. When the pilgrim exclaims, 'Now our journey is over!', he expresses the joy of one who has reached not only a geographical destination but also a spiritual one: the encounter with God in the city of his presence. Giving thanks to the Lord is Israel's vocation. Until the whole world recognises God, Israel is called to be the people of thanksgiving in the world, witnesses to divine faithfulness. Thus, every pilgrimage to Jerusalem renews Israel's mission: to give thanks, to praise and to show the way to other nations. The prophet Isaiah had foretold this universal plan: "At the end of days, the mountain of the Lord's temple will be firm on the top of the mountains, and all nations will flock to it... From Zion will go forth the law, and from Jerusalem the word of the Lord." (Is 2:2-3) Jerusalem then becomes a prophetic sign of the renewed world, where all peoples will be united in the same praise and the same peace. The Psalm recalls again: "There the thrones of judgement are set, the thrones of the house of David." With these words, Israel recalls the promise made by God to David through the prophet Nathan: "I will raise up a king from your descendants, and I will make his kingdom firm." (2 Sam 7:12). After the exile, there is no longer a king on the throne, but the promise remains alive: God does not go back on his word. In the celebrations at the Temple, this memory becomes prayer and hope: the day will come when God will raise up a king after his own heart, just and faithful, who will restore peace and justice. The very name Jerusalem means "city of peace." When we pray, "Pray for the peace of Jerusalem; may those who love you be secure" (Ps 122:6), we are not simply expressing a wish, but a profession of faith: only God can give true peace, and Israel is called to be a witness to this in the world. With the passing of the centuries, the hope for a righteous king is fulfilled in Jesus Christ, the Son of David. It is He who inaugurates the Kingdom of life and truth, of grace and holiness, of justice, love and peace, as proclaimed in the liturgy of the feast of Christ the King. In Him, the earthly Jerusalem becomes the new Jerusalem, the city of the definitive encounter between God and man. Every Eucharist is an ascent towards that city, a pilgrimage of the soul that ends in the heart of God. Israel's pilgrimage to Jerusalem then becomes a symbol of the journey of all humanity towards communion with God. And like the pilgrims of the Psalm, we too, the Church of the New Testament, can say with joy: "What joy when they said to me, 'We will go to the house of the Lord'."
*Second Reading from the letter of St. Paul the Apostle to the Colossians (1:12-20)
The invisible face of God. Once upon a time, there was a world that sought God but did not know how to see him. People looked up to the sky, built temples, offered sacrifices, but God remained invisible, distant. Then, one day, the Word became flesh: the God whom no one had ever seen took on a human face, and that face was that of Jesus of Nazareth. Since then, every time a man looks at Jesus, he looks at God. St Paul said it with words that sound like a song: "He is the image of the invisible God, the firstborn of all creation." In Him, everything that exists finds its origin and meaning. He is not only the beginning of the world, but also its heart: in Him everything was created, and in Him everything was reconciled. This plan of God did not come about yesterday, and Paul speaks of a design that has always been in place: 'He has delivered us from the power of darkness and transferred us to the Kingdom of the Son of his love.' God has always dreamed of a free, luminous human being, capable of communion. But what God had prepared in eternity was realised in time, in the present of Christ. This is why Paul writes: "In Him we have redemption, the forgiveness of sins." The mystery of Jesus is not a memory; it is a living reality that continues to work in the hearts of believers every day. God had made man "in His own image and likeness." But that image, in sin, had become clouded. So God Himself came to show us what it means to be human. In Jesus, man is restored to his original beauty. When Pilate shows him to the crowd and says, 'Behold the man!', he does not know that he is uttering a prophecy: in that wounded face, in that humble silence, the true man is revealed, as God had intended him to be. But in that face there is also the face of God. Jesus is the visibility of the invisible. He is God who allows himself to be seen, touched, heard. "Whoever has seen me has seen the Father," he will say to Philip. And Paul will add: "In him dwells all the fullness of the Godhead bodily." In Jesus, God and man meet forever. The infinite has taken flesh, heaven has become flesh. This is the mystery of the Cross. But how can the Cross be a sign of peace and reconciliation? Paul explains it this way: "God wanted to reconcile all things to himself, making peace through the blood of his cross." It is not God who wants the suffering of his Son. It is the hatred of men that kills him. Yet God transforms that hatred into redeeming love. It is the great reversal of history: violence becomes forgiveness, death becomes life, the cross becomes a tree of peace. We have seen men in history who have witnessed to peace and been killed for it — Gandhi, Martin Luther King, Itzhak Rabin, Sadat... — but only Christ, being both man and God, was able to transform evil into grace for the whole world. In his forgiveness of his crucifiers — “Father, forgive them” — God’s own forgiveness is revealed. From that day on, we know that no sin is greater than God’s love. On the cross, everything is accomplished. Paul writes: “God wanted all fullness to dwell in him, and through him to reconcile everything.” Creation finally finds its unity, its peace. The first to enter this Kingdom is the repentant thief: "Today you will be with me in paradise." And from then on, every person who opens themselves to forgiveness enters into that same light. The Eucharist is the heart of the mystery. Faced with such a gift, there is only one possible response: to give thanks. This is why Paul invites us: "Give thanks to God the Father, who has made you capable of sharing in the lot of the saints in the light." The Eucharist — in Greek, eucharistia means precisely "giving thanks" — is the place where the Church relives this mystery. Every Mass is a living memory of this reconciliation: God gives himself, the world is renewed, man finds himself again. It is there that everything is recomposed: the visible and the invisible, earth and heaven, man and God. And so, in the history of the world, a face has revealed the invisible. A pierced heart has brought peace. A broken loaf continues to make present the fullness of love. And every time the Church gathers for the Eucharist, Paul's song is renewed as a cosmic praise: Christ is the image of the invisible God, the first and the last, the one who reconciles the world with the Father, the one in whom everything subsists. In Him, everything finds meaning. In Him, everything is grace. In Him, the invisible God finally has a face: Jesus Christ, Lord of heaven and earth.
*From the Gospel according to Luke (23:35-43)
The logic of men and the logic of God. Three times, at the foot of the cross, the same provocation is repeated to Jesus: "If you are..." — "If you are the Messiah," the religious leaders mock; 'If you are the King of the Jews', sneer the Roman soldiers; 'If you are the Messiah', insults one of the criminals crucified with him. Each speaks from his own point of view: the leaders of Israel expect a powerful Messiah, but before them is a defeated and crucified man; the soldiers, men of earthly power, laugh at a defenceless 'king'; the criminal, on the other hand, awaits a saviour who will free him from death. These three voices recall the three temptations in the desert (Lk 4): even then, the tempter repeated, 'If you are the Son of God...'. Temptations of power, dominion and miracles. Jesus responded each time with the Word: 'It is written: man does not live on bread alone...' 'You shall worship the Lord your God and him alone shall you serve...' 'You shall not tempt the Lord your God'. Scripture was his strength to remain faithful to the mission of the poor and obedient Messiah. On the cross, however, Jesus is silent. He no longer responds to provocations. Yet he knows well who he is: the Messiah, the Saviour. But not according to the logic of men, who would like a God capable of saving himself, of dominating, of winning by force. Jesus dies precisely because he does not correspond to this human logic. His logic is that of God: to save by giving himself, without imposing himself. His silence is not empty, but full of trust. His very name, Jesus, means 'God saves'. He awaits his redemption from God alone, not from himself. The temptations are overcome forever: he remains faithful, totally surrendered into the hands of men, but trusting in the Father. Amidst the insults, two words encapsulate the mystery of the Cross. The first: "Father, forgive them, for they know not what they do." The second, addressed to the "good thief": "Today you will be with me in Paradise." Forgiveness and salvation: two gestures that are both divine and human. In Jesus, God himself forgives and reconciles humanity. The repentant thief — who turns to him and says, "Jesus, remember me when you come into your Kingdom" — is the first to understand who Christ truly is. He does not ask to come down from the cross, but to be welcomed. In that plea of humility and trust, the "remember" becomes the prayer that opens Paradise. Where Adam, in the Garden of Eden, had succumbed to the temptation to "be like God," Jesus, the new Adam, wins by waiting for everything from God. Adam had wanted to decide his own greatness and had been cast out of Paradise; Jesus, on the other hand, by accepting to be the Son in total abandonment, reopens Paradise to humanity. In the story of the Passion, two logics intersect: that of men, who seek a powerful God, and that of God, who saves through love and weakness. Jesus rejects the temptation to demonstrate his strength; instead, he chooses to trust the Father until the end. In his silence and forgiveness, divine power manifests itself as mercy. Beside him, the repentant thief becomes the first witness of the Kingdom: he recognises Christ as the true King, not of the powerful, but of the saved. Where Adam had closed the gates of Paradise, Jesus reopens them: 'Today you will be with me in Paradise' is God's definitive response to the logic of the world.
+ Giovanni D'Ercole
XXXIII Sunday in Ordinary Time C [16 November 2025]
First Reading from the Book of the Prophet Malachi (3:19-20a)
When Malachi wrote these words around 450 BC, the people were discouraged: faith seemed to be dying out, even among the priests of Jerusalem, who now celebrated worship in a superficial manner. Everyone asked themselves: 'What is God doing? Has he forgotten us? Life is unfair! The wicked succeed in everything, so what is the point of being the chosen people and observing the commandments? Where is God's justice?" The prophet then fulfils his task: to reawaken faith and inner energy. He rebukes priests and lay people, but above all he proclaims that God is just and that his plan of justice is advancing irresistibly. "Behold, the day of the Lord is coming": history is not a repeating cycle, but is moving towards fulfilment. For those who believe, this is a truth of faith: the day of the Lord is coming. Depending on the image that each person has of God, this coming can be frightening or arouse ardent expectation. But for those who recognise that God is Father, the day of the Lord is good news, a day of love and light. Malachi uses the image of the sun: "Behold, the day of the Lord is coming, burning like an oven." This is not a threat! At the beginning of the book, God says, "I love you" (Malachi 1:2) and "I am Father" (Malachi 1:6). The "furnace" is not punishment, but a symbol of God's burning love. Just as the disciples of Emmaus felt their hearts burning within them, so those who encounter God are enveloped in the warmth of his love. The 'sun of righteousness' is therefore a fire of love: on the day we encounter God, we will be immersed in this burning ocean of mercy. God cannot help but love, especially all that is poor, naked and defenceless. This is the very meaning of mercy: a heart that bends over misery. Malachi also speaks of judgement. The sun, in fact, can burn or heal: it is ambivalent. In the same way, the 'Sun of God' reveals everything, illuminating without leaving any shadows: no lie or hypocrisy can hide from its light. God's judgement is not destruction, but revelation and purification. The sun will 'burn' the arrogant and the wicked, but it will 'heal' those who fear his name. Arrogance and closed hearts will be consumed like straw; humility and faith will be transfigured. Pride and humility, selfishness and love coexist in each of us. God's judgement will take place within us: what is 'straw' will burn, what is 'good seed' will sprout in God's sun. It will be a process of inner purification, until the image and likeness of God shines within us. Malachi also uses two other images: that of the smelter, who purifies gold not to destroy it, but to make it shine in all its beauty; and that of the bleacher, who does not ruin the garment, but makes it shine. Thus, God's judgement is a work of light: everything that is love, service and mercy will be exalted; everything that is not love will disappear. In the end, only what reflects the face of God will remain. The historical context helps us to understand this text: Israel is experiencing a crisis of faith and hope after the exile; the priests are lukewarm and the people are disillusioned. The prophet's message: God is neither absent nor unjust. His 'day' will come: it is the moment when his justice and love will be fully manifested. The central image is the Sun of Justice, symbol of God's purifying love. Like the sun, divine love burns and heals, consumes evil and makes good flourish. In each of us, God does not condemn, but transforms everything into salvation by discerning what glorifies love and dissolves pride. Fire, the sun, the smelter and the bleacher indicate the purification that leads to the original beauty of man created in the image of God. Finally, there is nothing to fear: for those who believe, the day of the Lord reveals love. "The sun of righteousness shall rise with healing in its wings" (Malachi 3:20).
Responsorial Psalm (97/98:5-6, 7-8, 9)
This psalm transports us ideally to the end of time, when all creation, renewed, joyfully acclaims the coming of the Kingdom of God. The text speaks of the sea and its riches, the world and its inhabitants, the rivers and the mountains: all creation is involved. St Paul, in his Letter to the Ephesians (1:9-10), reminds us that this is God's eternal plan: 'to bring all things in heaven and on earth together under one head, Christ'. God wants to reunite everything, to create full communion between the cosmos and creatures, to establish universal harmony. In the psalm, this harmony is already sung as accomplished: the sea roars, the rivers clap their hands, the mountains rejoice. It is God's dream, already announced by the prophet Isaiah (11:6-9): 'The wolf shall dwell with the lamb, the leopard shall lie down with the kid... no one shall do evil or destruction on all my holy mountain'. But the reality is very different: man knows the dangers of the sea, conflicts with nature and with his fellow men. Creation is marked by struggle and disharmony. However, biblical faith knows that the day will come when the dream will become reality, because it is God's own plan. The role of prophets, such as Isaiah, is to revive the hope of this messianic Kingdom of justice and faithfulness. The Psalms also tirelessly repeat the reasons for this hope: Psalm 97(98) sings of the Kingdom of God as the restoration of order and universal peace. After so many unjust kings, a Kingdom of justice and righteousness is awaited. The people sing as if everything were already accomplished: "Sing hymns to the Lord who comes to judge the earth... and the peoples with righteousness." At the beginning of the psalm, the wonders of the past are recalled—the exodus from Egypt, God's faithfulness in the history of Israel—but now it is proclaimed that God is coming: his Kingdom is certain, even if not yet fully visible. The experience of the past becomes a guarantee of the future: God has already shown his faithfulness, and this allows the believer to joyfully anticipate the coming of the Kingdom. As Psalm 89(90) says: "A thousand years in your sight are like yesterday." And Saint Peter (2 Pt 3:8-9) reminds us that God does not delay his promise, but waits for the conversion of all. This psalm therefore echoes the promises of the prophet Malachi: "The sun of righteousness shall rise with healing in its wings" (Mal 3:20). The singers of this psalm are the poor of the Lord, those who await the coming of Christ as light and warmth. Once it was only Israel that sang: "Acclaim the Lord, all the earth, acclaim your king!" But in the last days, all creation will join in this song of victory, no longer just the chosen people. In Hebrew, the verb "to acclaim" evokes the cry of triumph of the victor on the battlefield ("teru'ah"). But in the new world, this cry will no longer be one of war, but of joy and salvation, because — as Isaiah says (51:8): "My righteousness shall endure forever, my salvation from generation to generation." Jesus teaches us to pray, "Thy Kingdom come," which is the fulfilment of God's eternal dream: universal reconciliation and communion, in which all creation will sing in unison the justice and peace of its Lord.
Second Reading from the Second Letter of Saint Paul the Apostle to the Thessalonians (3:7-12)
Saint Paul writes: "If anyone does not want to work, let him not eat" (2 Thessalonians 3:10). Today, this phrase cannot be repeated literally, because it does not refer to the unemployed of good will of our time, but to a completely different situation. Paul is not talking about those who cannot work, but those who do not want to work, taking advantage of the expectation of the imminent coming of the Lord to live in idleness. In Paul's world, there was no shortage of work. When he arrived in Corinth, he easily found employment with Priscilla and Aquila, who were in the same trade as him: tentmakers (Acts 18:1-3). His manual labour, weaving goat hair cloth, a skill he had learned in Tarsus in Cilicia, was tiring and not very profitable, but it allowed him not to be a burden to anyone: 'In toil and hardship, night and day we worked so as not to be a burden to anyone' (2 Thessalonians 3:8). This continuous work, supported also by the financial help of the Philippians, became for Paul a living testimony against the idleness of those who, convinced of the imminent return of Christ, had abandoned all commitment. His phrase 'if anyone does not want to work, let him not eat' is not a personal invention, but a common rabbinical saying, an expression of ancient wisdom that combined faith and concrete responsibility. The first reason Paul gives is respect for others: not taking advantage of the community, not living at the expense of others. Faith in the coming of the Kingdom must not become a pretext for passivity. On the contrary, waiting for the Kingdom translates into active and supportive commitment: Christians collaborate in the construction of the new world with their own hands, their own intelligence, their own dedication. Paul implicitly recalls the mandate of Genesis: 'Subdue the earth and subjugate it' (Gen 1:28), which does not mean exploiting it, but taking part in God's plan, transforming the earth into a place of justice and love, a foretaste of his Kingdom. The Kingdom is not born outside the world, but grows within history, through the collaboration of human beings. As Father Aimé Duval sings: "Your heaven will be made on earth with your arms." And as Khalil Gibran writes in The Prophet: "When you work, you realise a part of the dream of the earth... Work is love made visible." In this perspective, every gesture of love, care and service, even if unpaid, is a participation in the building of the Kingdom of God. To work, to create, to serve, is to collaborate with the Creator. Saint Peter reminds us: “With the Lord, one day is like a thousand years and a thousand years like one day... He is not slow in keeping his promise, but he is patient, wanting everyone to come to repentance” (2 Peter 3:8-9). This means that the time of waiting is not empty, but a time entrusted to our responsibility. Every act of justice, every good work, every gesture of love hastens the coming of the Kingdom. Therefore, the text concludes, if we truly desire the Kingdom of God to come sooner, we have not a minute to lose. Here is a small spiritual summary: Idleness is not simply a lack of work, but a renunciation of collaboration with God. Work, in whatever form, is part of the divine dream: to make the earth a place of communion and justice. Waiting for the Kingdom does not mean escaping from the world, but committing ourselves to transforming it. Every gesture of love is a stone laid for the Kingdom to come. Those who work with a pure heart hasten the dawn of the 'Sun of Justice' promised by the prophets.
From the Gospel according to Luke (21:5-19)
'Not a hair of your head will be lost.' This is prophetic language, not literal. We see every day that hair is indeed lost! This shows that Jesus' words are not to be taken literally, but as symbolic language. Jesus, like the prophets before him, does not make predictions about the future: he preaches. He does not announce chronicles of events, but keys of faith to interpret history. His discourse on the end of the Temple should also be understood in this way: it is not a horoscope of the apocalypse, but a teaching on how to live the present with faith, especially when everything seems to be falling apart. The message is clear: 'Whatever happens... do not be afraid!' Jesus invites us not to base our lives on what is passing. The Temple of Jerusalem, restored by Herod and covered with gold, was splendid, but destined to collapse. Every earthly reality, even the most sacred or solid, is temporary. True stability does not lie in stones, but in God. Jesus does not offer details about the 'when' or 'how' of the Kingdom; he shifts the question: 'Be careful not to be deceived...'. We do not need to know the calendar of the future, but to live the present in faithfulness. Jesus warns his disciples: "Before all this, they will persecute you, they will drag you before kings and governors because of my Name." Luke, who writes after years of persecution, knows well how true this is: from Stephen to James, from Peter to Paul, to many others. But even in persecution, Jesus promises: "I will give you a word and wisdom that no one will be able to resist." This does not mean that Christians will be spared death — "they will kill some of you" — but that no violence can destroy what you are in God: "Not a hair of your head will be lost." It is a way of saying: your life is kept safe in the hands of the Father. Even through death, you remain alive in God's life. Jesus twice uses the expression "for my Name's sake." In Hebrew, "The Name" refers to God himself: to say "for the Name's sake" is to say "for God's sake." Thus Jesus reveals his own divinity: to suffer for his Name is to participate in the mystery of his love. In the Acts of the Apostles, Saint Luke shows Peter and John who, after being flogged, "went away rejoicing because they had been counted worthy of suffering for the Name of Jesus" (Acts 5:41). It is the same certainty that Saint Paul expresses in his Letter to the Romans: "Neither death nor life, nor any creature can separate us from the love of God in Christ Jesus" (Rom 8:38-39). Catastrophes, wars, epidemics — all these "shocks" of the world — must not take away our peace. The true sign of believers is the serenity that comes from trust. In the turmoil of the world, the calmness of God's children is already a testimony. Jesus sums it up in one word: "Take courage: I have overcome the world!" (Jn 16:33). And here is a spiritual synthesis: Jesus does not promise a life without trials, but a salvation stronger than death. Not even a hair...' means that no part of you is forgotten by God. Persecution does not destroy, but purifies faith. Nothing can separate us from the love of God: our security is the risen Christ. To believe is to remain steadfast, even when everything trembles.
+ Giovanni D'Ercole
Christ the King: «Today with Me in the Paradise». Love and vinegar
TRAUMATIC OR PRECARIOUS EXPERIENCES. «DARKNESS»: APATHY, DEPRESSION, PSYCHOSIS, HOSTILITY - (by Francesco Giovannozzi, psychologist and psychotherapist)
A look into the «darkness».
As I have already mentioned, many poets and writers have described the flow of the human soul.
Eugenio Montale expresses this in one of his poems from 1925, on the pain of living, providing us with the image of a stream that cannot flow, a leaf crumpled by excessive heat, a horse exhausted on the ground.
These are images that linger in our minds, leaving us with food for thought and questions to ponder.
There have been moments of 'darkness' in our lives, and perhaps there will be more.
Feelings of discouragement and not knowing which path to take - each of us has experienced this first-hand.
The intensity and duration of the 'darkness' vary depending on the circumstances and our personal ability to react.
We react differently to defeat or disappointment; what upsets one person may leave another completely indifferent.
An encounter with 'darkness' can be common when faced with serious difficulties such as bereavement, loss of employment, the onset of illness, the end of a relationship, and so on.
This state of mind is temporary and ends spontaneously, without bringing about changes in a person's life.
In other cases, it is important not to underestimate this state of mind, as it could be a sign of psychosomatic or psychological distress.
In these cases, we often experience inexplicable feelings of worry and apathy, and we feel more fatigued.
Let us remember that the reaction to 'darkness' often follows a traumatic experience, which in ordinary circumstances would not have caused any temporary feelings of low mood.
A more severe and prolonged reaction, one that the individual cannot overcome on their own, is an unusual condition.
In older people, emotional shocks can trigger moments of 'darkness' more easily than in younger people.
Sometimes older people are marginalised, have fewer social relationships, and often suffer a loss of prestige, especially when they lose hope.
But even adolescents [with their precariousness] are not immune to these moments of unease.
It is not true that adolescence is a happy time of life; on the contrary, it is perhaps one of the most troubled.
In these moments of 'darkness', which clinicians call «depression», we notice that people going through this phase greatly reduce their activities, have less self-confidence, and take an interest in few things.
They are able to keep their jobs even if they have to work harder. Usually, their memory and relationship with reality are not altered - unless a serious condition («psychosis») has arisen.
Arieti describes the depression we have called 'darkness' here as a combination of sadness and pessimism.
The latter is the essential element of the combination; the unhealthy idea is to believe that what has happened to a person will always happen to them, or that their state of mind will never change.
Defeatism, the illusion of knowing what will happen to us in the future, consolidates sadness into 'darkness'.
Often the 'darkness' of the soul is discharged onto the body.
We may experience weight loss, feelings of oppression in the heart, decreased bodily secretions, insomnia, and frequent headaches.
In our behaviour towards others, 'darkness' makes us tend to exploit and influence others; it makes us unwilling to be persuaded. We find it difficult to satisfy others, and hostility often overwhelms us.
Faber Andrew wrote a poem entitled “To those who are going through their darkness”...
The poet invites the reader to «believe in poetry. In the eyes of those who have already found that road».
Then again: «There is a sky here waiting for you, with a breathtaking panorama of dreams».
For a poet, poetry is the main road, but we who are not poets have something to believe in, and that is the pillar of our reality.
Let us always remember that when the night reaches its darkest point, the dawn of a new day begins.
Francesco Giovannozzi, psychologist and psychotherapist.
AGITATION, RESTLESSNESS, WORRIES, FEAR - (by Francesco Giovannozzi, psychologist and psychotherapist)
In today's society, there are many factors that cause anxiety and restlessness, and strategies to combat them are often difficult to find.
This period is characterised by the 'shaking' of fundamental values, norms and aspirations that drove man towards fulfilment and healthy relationships with others.
The current wars around the world, the memories of them for older people, and the threat of nuclear war add to the list.
In such a hostile climate, human isolation is accentuated.
Each person has their own way of reacting: the most common is a sense of unease, anxiety, feeling in danger without knowing what the danger is; a sense of ruin, or something else.
We often fail to understand the cause of all this. People feel helpless, and if this unease is strong, it can be discharged onto the body.
Muscle stiffness may be noticed, or there may be tremors, a feeling of weakness or tiredness; even the voice may tremble.
At the cardiovascular level, palpitations, fainting, increased heart rate and increased blood pressure may occur.
Nausea, vomiting and stomach ache may also occur in the intestines, which have no organic origin.
There may also be other symptoms typical of each person's history, and there is no organ that cannot be affected by internal tension.
I remember that in my professional life I have met people with psychological problems that were 'discharged' in different parts of the body, sometimes in the most unimaginable places.
I have encountered alopecia (hair loss), locked limbs, visual disturbances, fainting, and more recently, teenagers who cut themselves...
If a person feels overwhelmed by a sudden wave of inner discomfort, they may react inappropriately or even dangerously (alcohol, drugs, speeding, gambling, etc.).
Understanding these disturbances, worries and anxieties is important in determining whether they are normal or not.
Unusual states of anxiety are distinguished from more or less persistent apprehension with acute crises.
These states are to be distinguished from the state of generalised worry that we find common in our daily lives.
Let us remember that in order to define our anxiety and agitation, we must convince ourselves that it is something normal when the individual feels threatened.
Agitation should be distinguished from fear, where the danger is real: the individual can assess the situation and choose whether to face it or flee.
When we talk about agitation in the normal sense, we mean that it is human nature to feel it when faced with danger, illness, etc.
It represents the deepest way of living our human existence.
It makes us face our limits and weaknesses, which are not manifestations of inner discomfort or illness, but expressions of human nature.
The more aware we are of our limits, the better we are able to live with our anxieties.
For our fellow human beings who feel omnipotent, agitation and anxiety are unbearable, as they bring to consciousness the limits that are a wound to their 'feeling of being a superior creature'.
We experience normal unease even when we leave an 'old road for a new one'.
From this point of view, it accompanies us in our changes, in our evolution, and in finding meaning in our lives.
Dr Francesco Giovannozzi, psychologist and psychotherapist
In the divine attitude justice is pervaded with mercy, whereas the human attitude is limited to justice. Jesus exhorts us to open ourselves with courage to the strength of forgiveness, because in life not everything can be resolved with justice. We know this (Pope Francis)
Nell’atteggiamento divino la giustizia è pervasa dalla misericordia, mentre l’atteggiamento umano si limita alla giustizia. Gesù ci esorta ad aprirci con coraggio alla forza del perdono, perché nella vita non tutto si risolve con la giustizia; lo sappiamo (Papa Francesco)
The true prophet does not obey others as he does God, and puts himself at the service of the truth, ready to pay in person. It is true that Jesus was a prophet of love, but love has a truth of its own. Indeed, love and truth are two names of the same reality, two names of God (Pope Benedict)
Il vero profeta non obbedisce ad altri che a Dio e si mette al servizio della verità, pronto a pagare di persona. E’ vero che Gesù è il profeta dell’amore, ma l’amore ha la sua verità. Anzi, amore e verità sono due nomi della stessa realtà, due nomi di Dio (Papa Benedetto)
“Give me a drink” (v. 7). Breaking every barrier, he begins a dialogue in which he reveals to the woman the mystery of living water, that is, of the Holy Spirit, God’s gift [Pope Francis]
«Dammi da bere» (v. 7). Così, rompendo ogni barriera, comincia un dialogo in cui svela a quella donna il mistero dell’acqua viva, cioè dello Spirito Santo, dono di Dio [Papa Francesco]
The mystery of ‘home-coming’ wonderfully expresses the encounter between the Father and humanity, between mercy and misery, in a circle of love that touches not only the son who was lost, but is extended to all (Pope John Paul II)
Il mistero del ‘ritorno-a-casa’ esprime mirabilmente l’incontro tra il Padre e l’umanità, tra la misericordia e la miseria, in un circolo d’amore che non riguarda solo il figlio perduto, ma si estende a tutti (Papa Giovanni Paolo II)
The image of the vineyard is clear: it represents the people whom the Lord has chosen and formed with such care; the servants sent by the landowner are the prophets, sent by God, while the son represents Jesus. And just as the prophets were rejected, so too Christ was rejected and killed (Pope Francis)
L’immagine della vigna è chiara: rappresenta il popolo che il Signore si è scelto e ha formato con tanta cura; i servi mandati dal padrone sono i profeti, inviati da Dio, mentre il figlio è figura di Gesù. E come furono rifiutati i profeti, così anche il Cristo è stato respinto e ucciso (Papa Francesco)
‘Lazarus’ means ‘God helps’. Lazarus, who is lying at the gate, is a living reminder to the rich man to remember God, but the rich man does not receive that reminder. Hence, he will be condemned not because of his wealth, but for being incapable of feeling compassion for Lazarus and for not coming to his aid. In the second part of the parable, we again meet Lazarus and the rich man after their death (vv. 22-31). In the hereafter the situation is reversed [Pope Francis]
“Lazzaro” significa “Dio aiuta”. Lazzaro, che giace davanti alla porta, è un richiamo vivente al ricco per ricordarsi di Dio, ma il ricco non accoglie tale richiamo. Sarà condannato pertanto non per le sue ricchezze, ma per essere stato incapace di sentire compassione per Lazzaro e di soccorrerlo. Nella seconda parte della parabola, ritroviamo Lazzaro e il ricco dopo la loro morte (vv. 22-31). Nell’al di là la situazione si è rovesciata [Papa Francesco]
duevie.art
don Giuseppe Nespeca
Tel. 333-1329741
Disclaimer
Questo blog non rappresenta una testata giornalistica in quanto viene aggiornato senza alcuna periodicità. Non può pertanto considerarsi un prodotto editoriale ai sensi della legge N°62 del 07/03/2001.
Le immagini sono tratte da internet, ma se il loro uso violasse diritti d'autore, lo si comunichi all'autore del blog che provvederà alla loro pronta rimozione.
L'autore dichiara di non essere responsabile dei commenti lasciati nei post. Eventuali commenti dei lettori, lesivi dell'immagine o dell'onorabilità di persone terze, il cui contenuto fosse ritenuto non idoneo alla pubblicazione verranno insindacabilmente rimossi.