Second Sunday in Ordinary Time (year A) [18 January 2026]
May God bless us and may the Virgin protect us. Today begins the week of prayer for Christian unity (18-25 January) and Ordinary Time resumes.
First Reading from the Book of the Prophet Isaiah (49:3-6)
This passage belongs to a group of four texts from the prophet Isaiah, called the "Songs of the Servant". They date back to the dramatic period of the Babylonian Exile (6th century BC) and are addressed to a discouraged people who wonder if God has forgotten them. The prophet, however, announces a decisive word: Israel is still God's servant. The Covenant is not broken; God has not only not abandoned his people, but entrusts them with an even greater mission. In this song, the Servant is not a particular individual, but the people of Israel as a whole, as the text clearly states: 'You are my servant, Israel'. Its vocation is equally clear: to manifest the glory of God. This glory is not abstract, but concrete: it is God's work of salvation, identified here with the return from exile. The liberation of the people will be the visible proof that God is the saviour. Thus, those who have been saved become witnesses of salvation before the world. In the ancient mindset, the defeat and deportation of a people could seem like the failure of their God; liberation, on the other hand, will manifest to the pagan peoples the superiority of the God of Israel. Being a "servant" therefore means, on the one hand, the certainty of God's support and, on the other, a mission: to continue to believe in salvation and to bear witness to it, so that other peoples may also recognise God as saviour. This explains the final announcement: 'I will make you a light to the nations, that my salvation may reach to the ends of the earth'. God's plan concerns not only Israel but all humanity. Here, the messianic expectation evolves profoundly: the Messiah is no longer an individual king but a collective subject, the people of Israel, who do not exercise political power but carry out a mission of service. One difficulty remains: if the Servant is Israel, how can he "gather Israel"? Isaiah is actually addressing the "Remnant," the small group of faithful who did not lose their faith during the exile. This Remnant has the task of bringing the people back to God, that is, of converting them. But this is only the first stage: the rise of Israel becomes the initial sign of the plan of universal salvation. Finally, the prophet insists on the divine origin of this message: it is not the fruit of human invention, but the word of the Lord. In the midst of discouragement, a confession of humble and profound trust resounds: the Servant's strength is not in himself, but in God.
decisive role of the faithful Remnant. +The foundation of everything: strength comes from God alone, not from man.
*Responsorial Psalm (39/40)
The statement in Psalm 39/40 – "sacrifice and offering you do not desire" is surprising, because the psalms were sung in the temple itself, while sacrifices were being offered. In reality, the meaning is clear: what matters to God is not the ritual itself, but the attitude of the heart that it expresses. This is why the psalmist can say: "You have opened my ears"... then I said: "Here I am, I am coming". The whole Bible recounts a long educational journey in understanding sacrifice, which goes hand in hand with the revelation of the true face of God. To sacrifice means "to make sacred", to enter into communion with God; but the way of doing so changes as we understand who God really is. Israel did not invent sacrifice: it was a common practice among the peoples of the Near East. However, from the beginning, biblical faith introduces a decisive difference: human sacrifices are absolutely forbidden. God is the God of life, and cannot ask for death in order to draw closer to Him. Even the story of Abraham and Isaac shows that 'sacrificing' does not mean killing, but offering. Over the centuries, a true conversion of sacrifice took place, concerning first and foremost its meaning. If God is thought of as a being to be appeased or bought, sacrifice becomes a magical gesture. If, on the other hand, God is recognised as the one who loves first and gives freely, then sacrifice becomes a response of love and gratitude, a sign of the Covenant and not a commodity to be exchanged. Biblical pedagogy thus leads from the logic of 'giving in order to receive' to the logic of grace: everything is a gift, and man is called to respond with the 'sacrifice of the lips', that is, with thanksgiving. The substance of sacrifice also changes: the prophets teach that the true sacrifice pleasing to God is to give life, not to give death. As Hosea says (6:6): 'I desire mercy, not sacrifice'. The ultimate ideal is the service of our brothers and sisters, expressed in the Songs of the Servant of Isaiah: a life given so that others may live. Psalm 39/40 summarises this journey: God opens man's ear to enter into a dialogue of love; in the New Covenant, sacrifice becomes totally spiritual: 'Behold, I come'.
*Second Reading from the First Letter of Saint Paul the Apostle to the Corinthians (1:1-3)
This text celebrates the dignity of those of us who are baptised. It is chosen for this Sunday, which marks the return to ordinary time in the liturgy: ordinary does not mean trivial, but simply in the order of the year. Every Sunday we celebrate extraordinary events: here St Paul reminds us of the greatness of our title as Christians. According to Paul, we are those who invoke the name of the Lord Jesus Christ, recognising him as God. To say 'Lord' means that Jesus is the centre of our life, of history and of the world. This is why Paul calls us 'holy people': being holy does not mean being perfect, but belonging to God. Baptism consecrates us to Him, and the community deserves to be honoured in the Eucharistic celebration. If Jesus is not truly our Lord, we must question our faith. Paul emphasises the name of Christ several times in his letter, showing that our relationship with Him is the foundation of Christian life. All Christians are 'called': Paul himself did not choose to be an apostle, but was called by God on the road to Damascus. The word Church (ecclesia) means 'called', and every local community is called to reflect God's universal love. The mission is universal, but accessible: God does not ask us for extraordinary gestures, only willingness to do His will, as today's Psalm reminds us: 'Behold, I am coming'. The Eucharistic liturgy echoes Paul's words: in the gesture of peace and in the greeting 'The Lord be with you', we are immersed in the grace and peace of Christ. This text is particularly suitable for the week of prayer for Christian unity: it reminds us of what unites Christians throughout the world, called to be seeds of a new humanity, which one day will be reunited in grace and peace around Jesus Christ. The historical context of this letter: Corinth was a city of great wealth and poverty, a crossroads between the Adriatic and the Aegean, with a mixed population and marked social contrasts. The Christian community founded by Paul reflected these differences. The letter to the Corinthians that we read today is probably the first to have come down to us, written around 55-56 AD, in response to specific questions from the community.
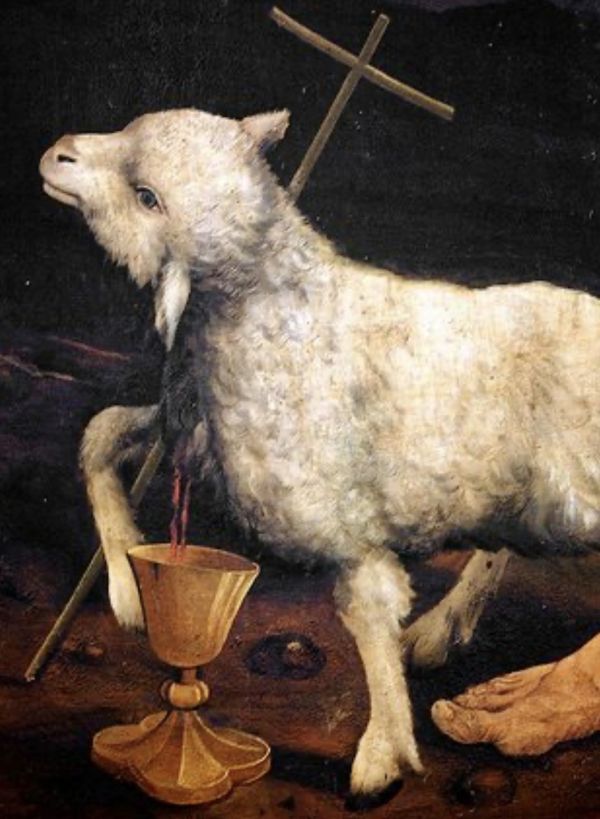
From the Gospel according to John (1:29-34)
John the Baptist solemnly proclaims: "I have seen and testified that this is the Son of God." At that time, the title "Son of God" was synonymous with Messiah: to recognise this in Jesus meant to announce the Messiah awaited by Israel. Every king of Jerusalem received the anointing and the title of Son of God as a sign that the Spirit was guiding him; but unlike previous kings, Jesus is the one on whom the Spirit 'sleeps' permanently, indicating that his entire mission will be led by the Holy Spirit. John the Baptist also describes Jesus as 'the Lamb of God who takes away the sin of the world'. The figure of the lamb evokes three images: the Paschal Lamb, a sign of liberation; Isaiah's Suffering Servant, innocent and bearing the sins of others; the lamb offered by God, as in Abraham's trial with Isaac. Jesus is therefore the Messiah, the liberator of humanity, but he does not immediately eliminate sin: he offers us the possibility of freeing ourselves from it by living guided by the Spirit, with love, generosity and forgiveness. Salvation is not for one man alone, but for all believers, the 'Body of Christ'. The new humanity begins in Jesus, through his obedience and his full communion with God, offering a model of new life.
*Origen, in his commentary on the Gospel of John, writes: 'Thus John calls Jesus the Lamb of God: "Behold the Lamb of God who takes away the sins of the world." With these words, John declares that Christ, the one who was before him, is the one who takes away the sins of the world.
+Giovanni D'Ercole